Panamax sloop Nilaya has departed from her construction hall at the builder’s Vollenhove facility in preparation for the installation of her towering rig in Amsterdam. Nilaya’s racy, low profile with its straight bow, wide transom, and twin rudders, echoes the look of her owners’ previous highly successful maxi-racer of the same name. Not surprisingly, she is from the boards of the same naval architecture and design firms, Reichel / Pugh and Nauta, both firms with impressive reputations for high-performance sailing yachts.
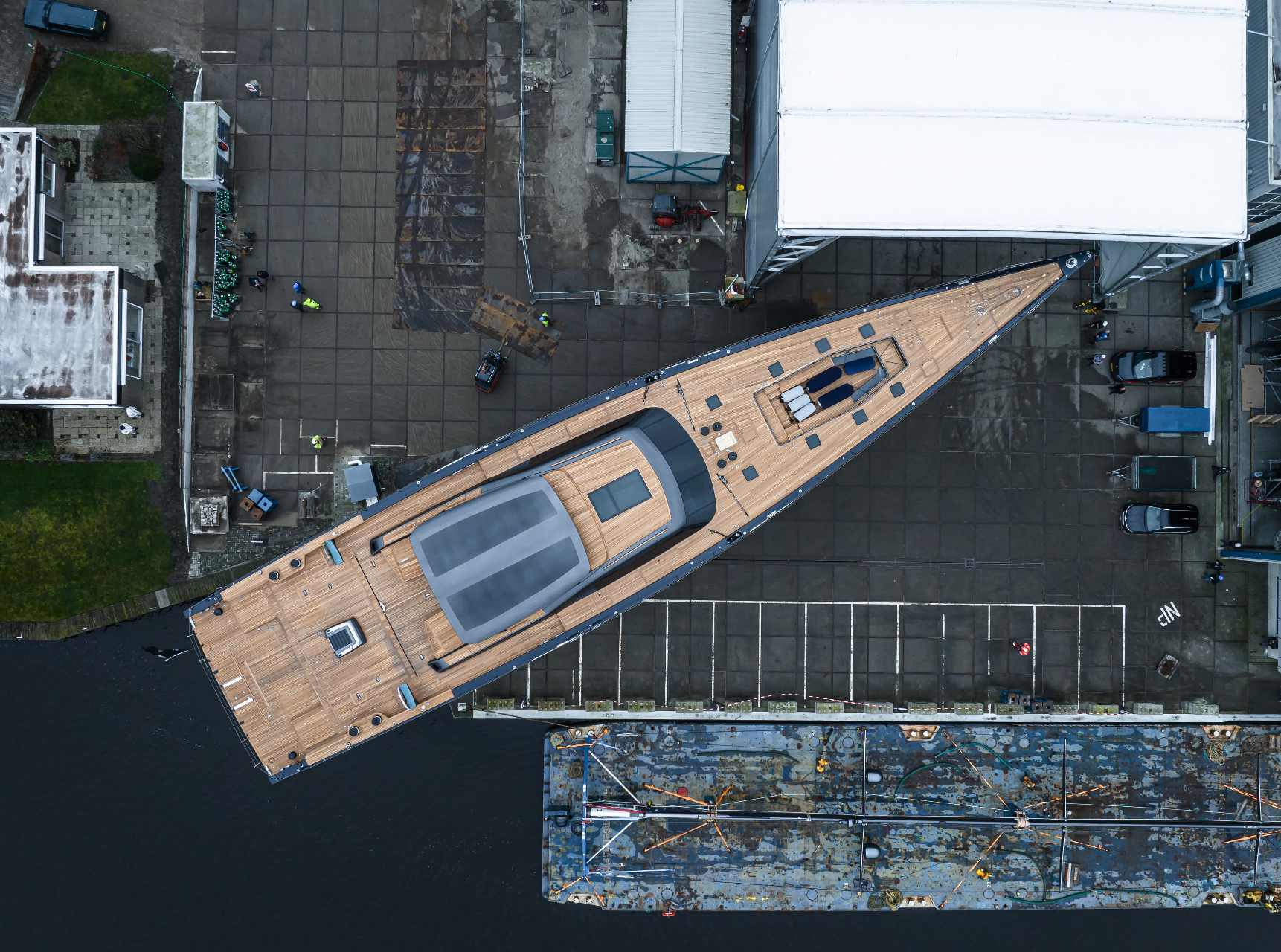

Exploring all the options for a luxurious performance cruiser also capable of podium finishes at superyacht regattas, the team made full design studies for the yacht in both carbon and aluminum using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to optimize hull shape and balance. Royal Huisman’s Featherlight™ method, an evolution of nearly 60 years of aluminum yacht-building experience melded with the latest carbon technology, provides her owners the best of both materials for a no-compromise yacht.
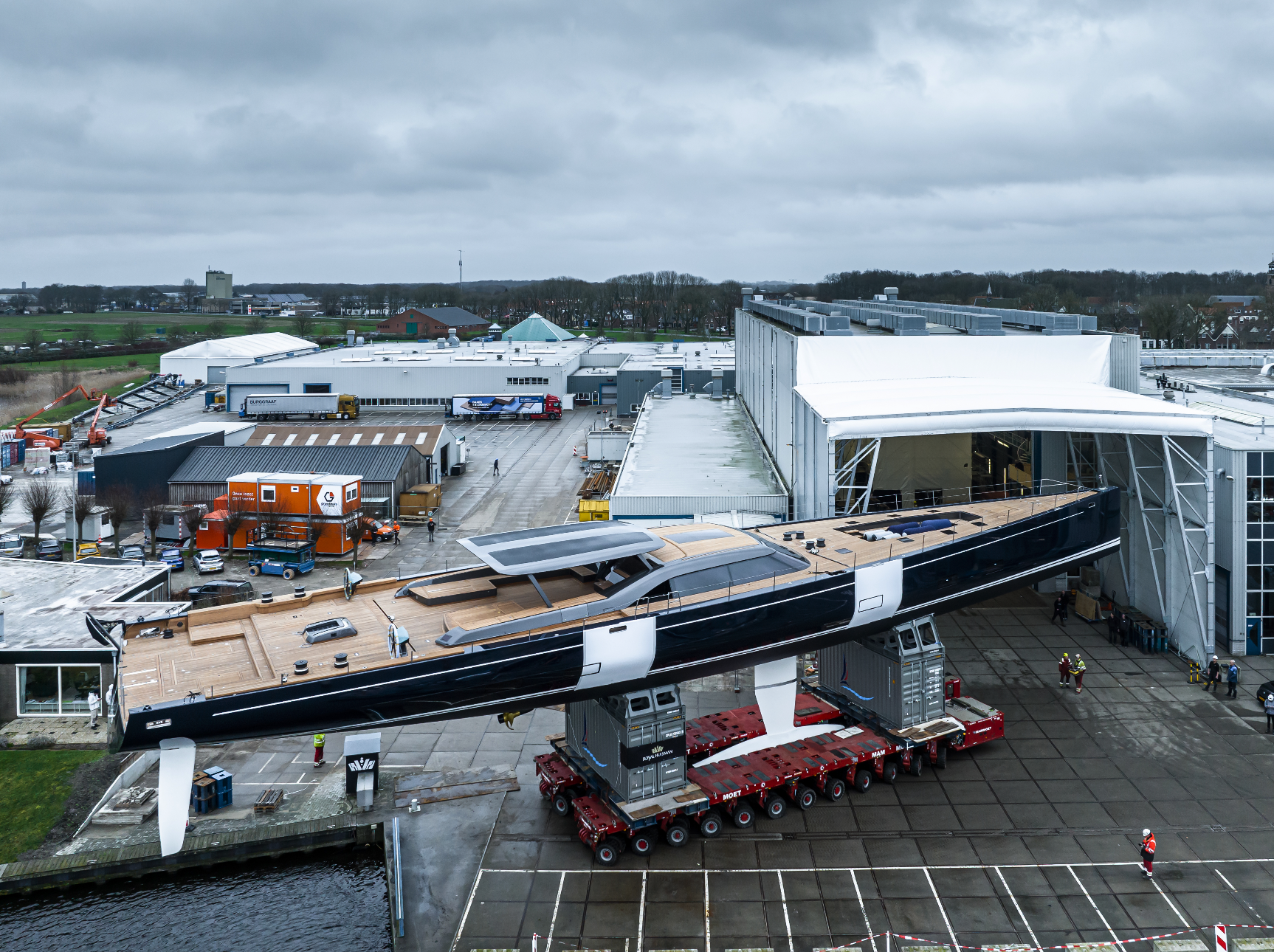

Nauta Design’s Mario Pedol noted that the choice of primary hull material did not fundamentally change the yacht’s layout or total weight. “With Reichel / Pugh, we set the target weight. Royal Huisman really embraced the concept. It was a very good process, good collaboration.”
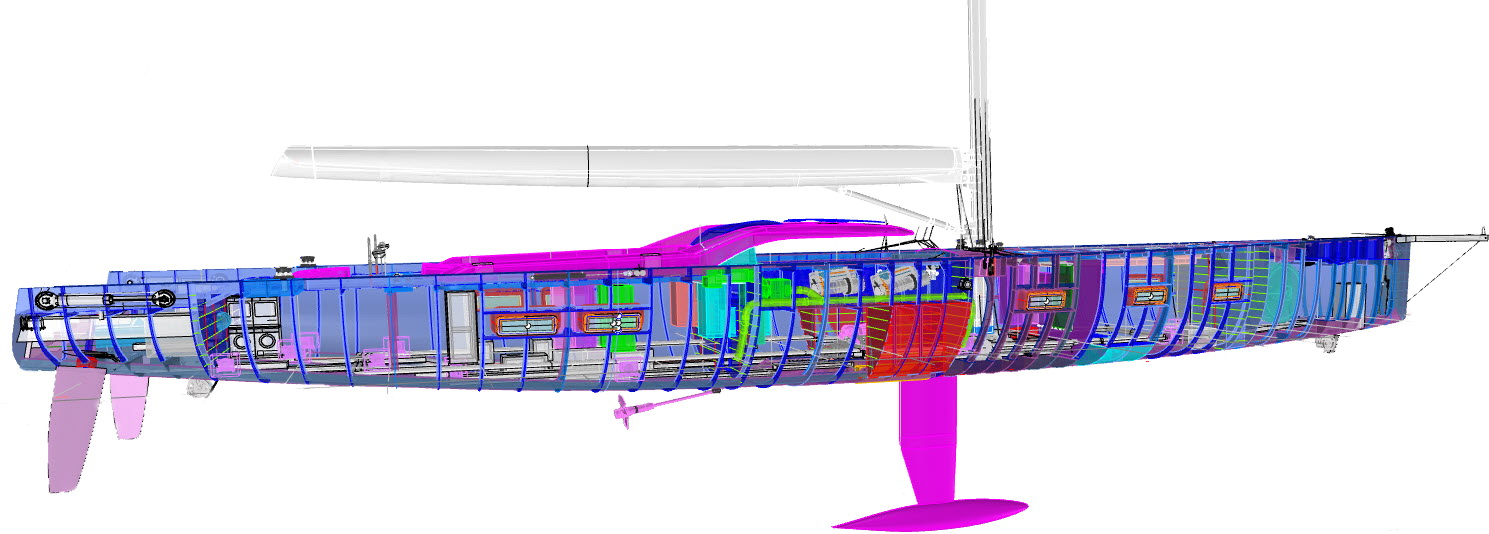
The Featherlight™ process makes use of Finite Element Analysis (FEA), a design methodology rooted in spacecraft technology. FEA modeling enabled selecting various construction materials and varied Alustar aluminum plate thicknesses and frame spacing to maximize hull stiffness while minimizing total displacement. With engineering and weight management brought in-house, the approach was comprehensive, extending to lighting, insulation, and all mechanical systems. The interior, too, benefited from careful weight analysis. All interior structural members utilize lightweight foam coring.

Capturing the carbon fiber expertise of its sister company Rondal, Royal Huisman’s engineering team used this synergy to analyze and predict which structural components would be best made of composites or aluminum. For example, the entire 17.5m / 57-foot curvaceous coachroof and guest cockpit structure are carbon composite. Likewise, the recessed tender well on the foredeck (that transforms to a seating area for cruising or a flush deck for racing) is also carbon composite as are a watertight bulkhead, crew entrance, twin rudders, the keel trunk and a cockpit bimini hardtop.
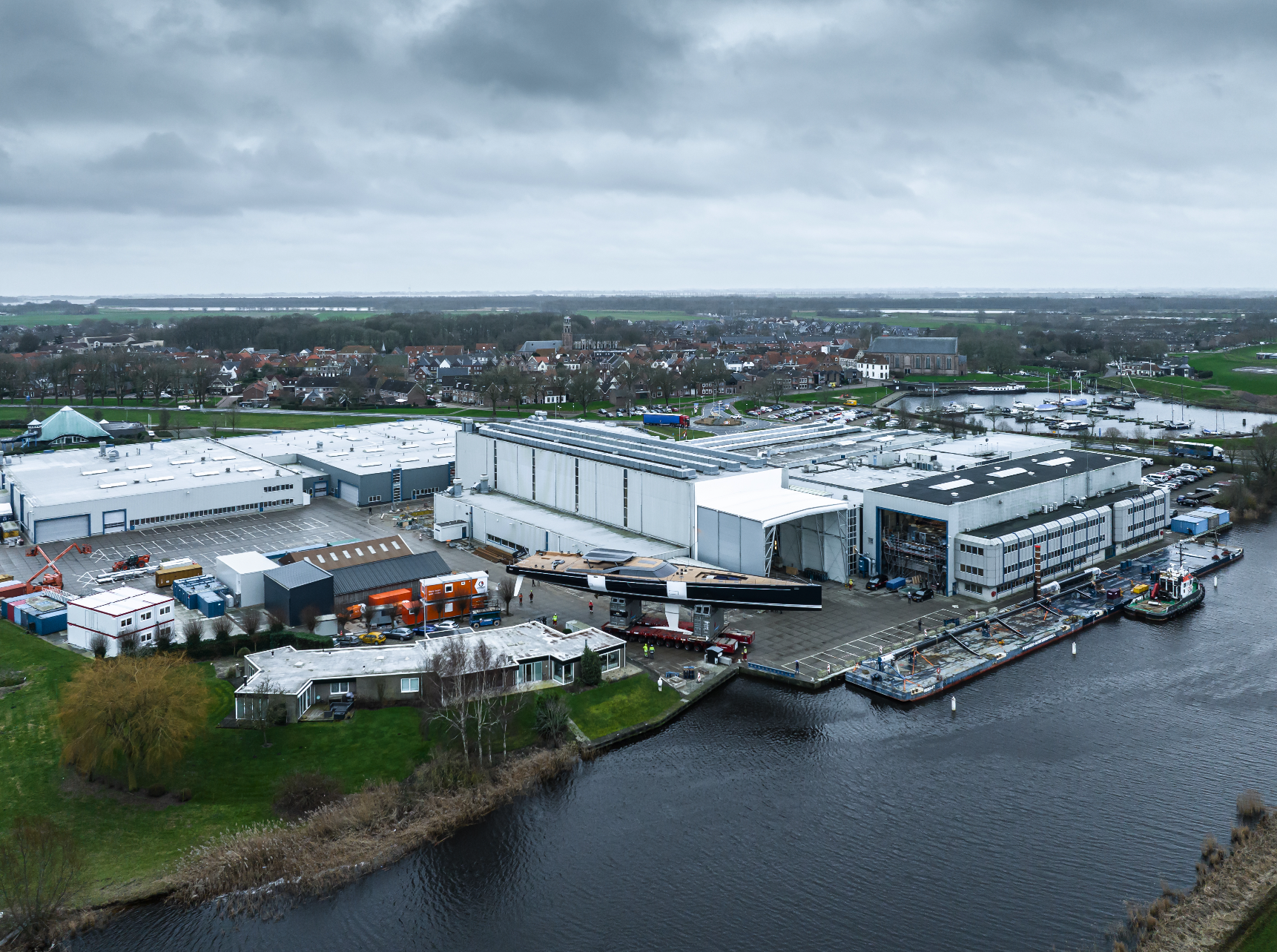

Project 405 is also the first yacht of this size range designed to take advantage of structured luff sail design pioneered by Doyle Sails, a choice that allowed the entire Rondal mast, rig, and components to be lighter — a key point considering her Panamax air draft. To take advantage of the very narrow headsail sheeting angles possible, Rondal created a radical new curved carbon fiber spreader design that is both shorter and more aerodynamic than anything previously available. Rondal also supplied new generation hybrid (carbon and aluminum) captive winches, hatches and various sail handling gear. Most deck hardware is titanium.
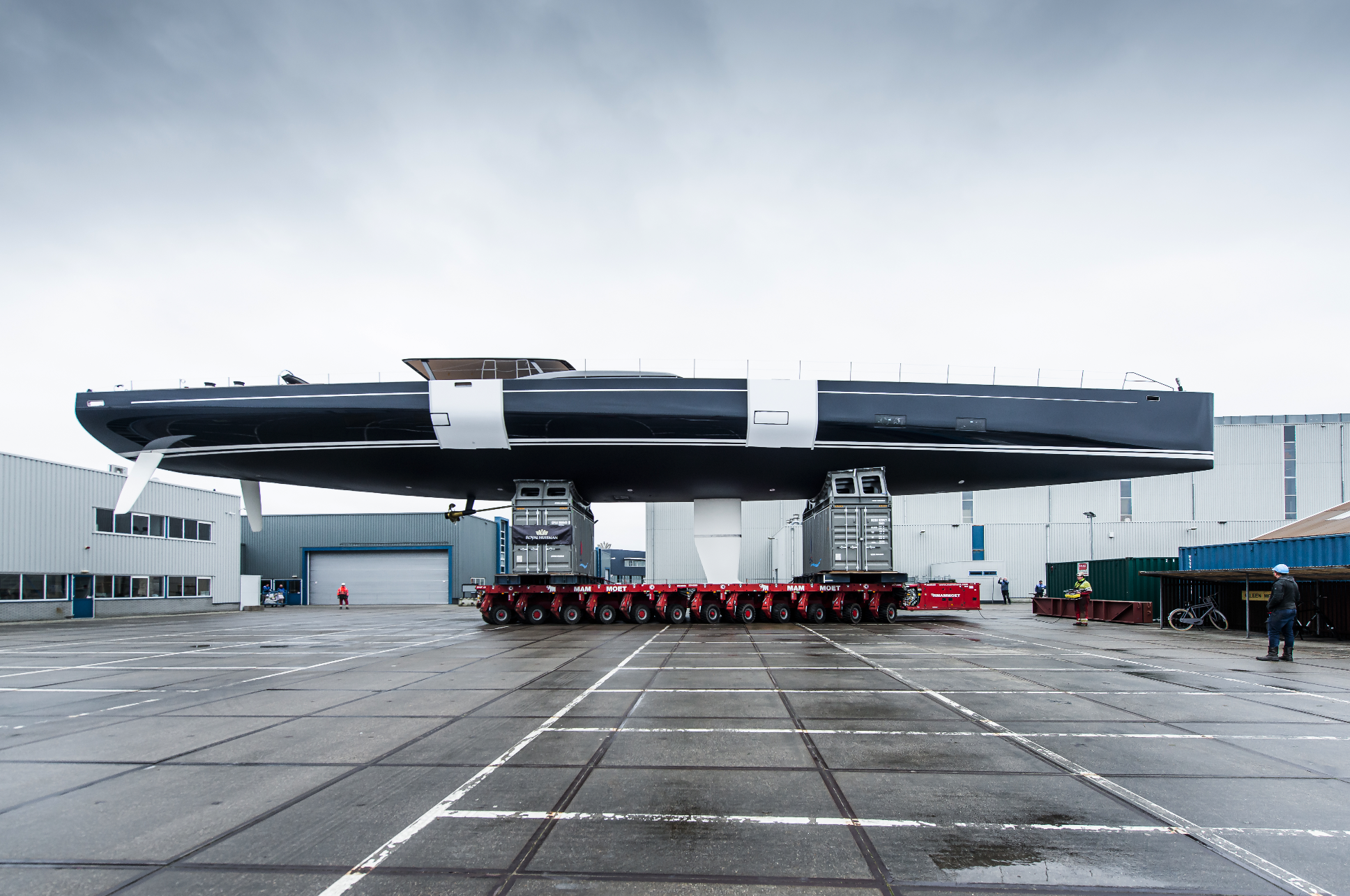

"The success of the innovations with Project 405 paves the way to use this bold new approach for future builds. I am proud of the investment we have made in advanced engineering and of the way teams from Royal Huisman and Rondal advanced new solutions to meet the brief from very knowledgeable clients and designers. The owners as well deserved congratulations for pushing everyone to achieve just a little bit more and for encouraging innovation at every step. Nilaya will be the world’s lightest aluminum sailing superyacht for her length: she rewrites the script for high-performance superyachts,” says Jan Timmerman, Royal Huisman CEO.
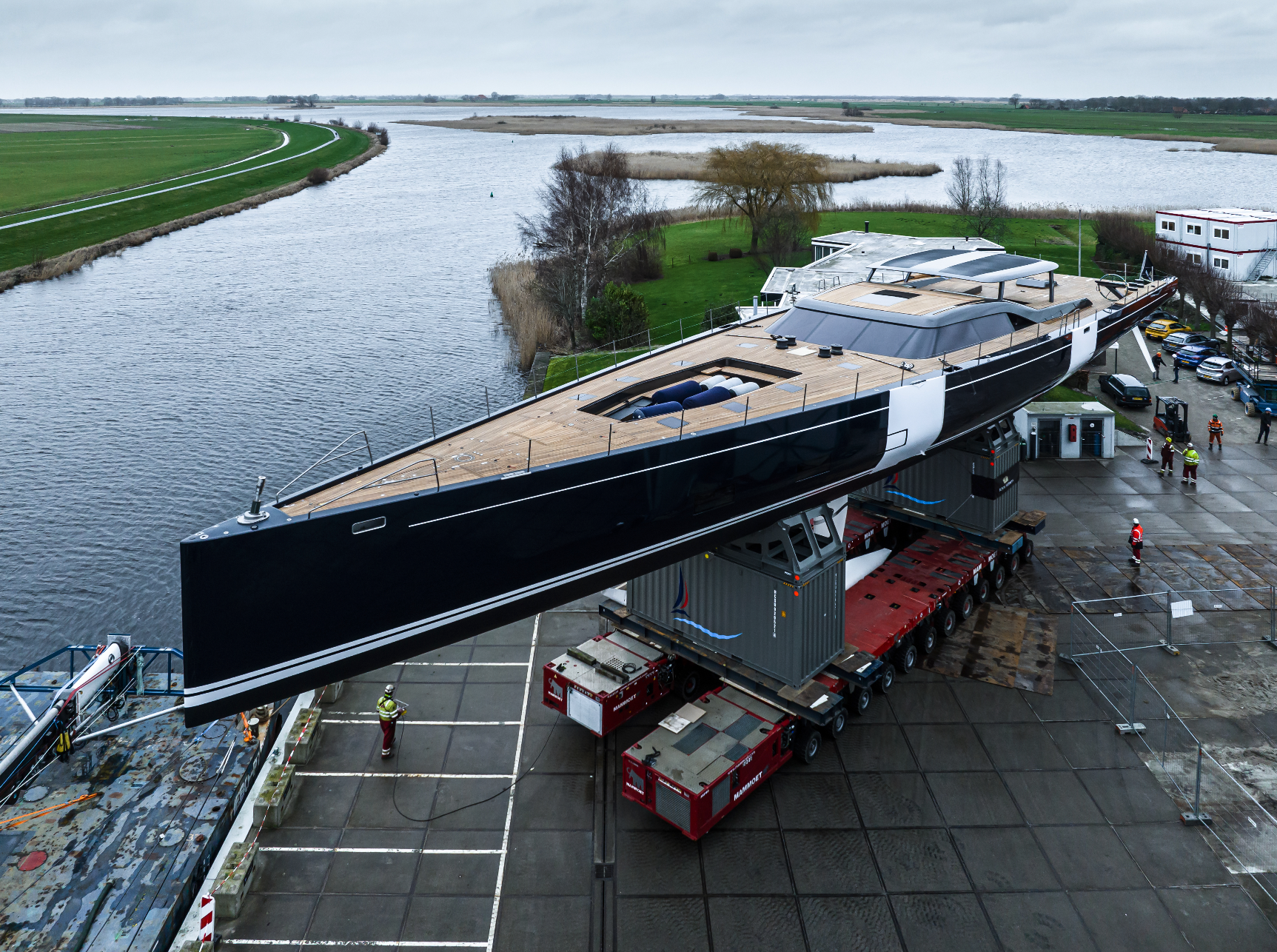

The 46.8-meter Project 405 Nilaya will be delivered to her owners in the coming months.
Royal Huisman is a Dutch shipyard established in 1884 in Ronduite, building and refitting custom luxury sailing and motor yachts at its shipyard in Vollenhove, the Netherlands.
Credits: Tom van Oossanen/Royal Huisman





